Hair transplantation
Hair transplantation is a good surgical technique that involves removing healthy hair growth from certain areas of
the body and transferring them to parts of the top where they are thinning out. The procedure is one of the
effective methods of treating male-pattern baldness.
Generally known as hair implantation, a hair transplant can be achieved using two different techniques: follicular
unit extraction or the removal and transplantation of a follicular unit one at a time, or follicular unit strip surgery
in which a strip of scalp is removed and split into several micrografts which contain small bits of hair.
Hair transplant is an operation that can be completed on men and women who suffer from a specific degree of
hair thinning, although men tend to develop it more regularly and earlier than women. Male-pattern baldness or
androgenetic alopecia, for instance, virtually all occurs among men beginning at age 35. Some cases possess
reported the condition on males as young as twenty years old.
Hair transplantation can be recommended to anyone whose long-lasting or temporary hair thinning is caused by the following:
• Genetics –
Male-pattern baldness is generally connected with genetics, particularly a person’s sensitivity to the
by-item of testosterone named dihydrotestosterone, which may interfere in the manner the hair roots shrink and allow the hair to increase.
• Underlying conditions –
Some patients have problems with particular types of autoimmune diseases, such as
lupus, where the body’s own disease-fighting capability treats the progress of hair in the follicles as a threat,
thereby avoiding it from growing or making it susceptible to fall off quickly.
• Medications –
Certain drugs, such as those that are used in chemotherapy, could cause hair loss being that they
are built to eliminate all sorts of cells, especially the ones that divide at an extremely rapid rate.
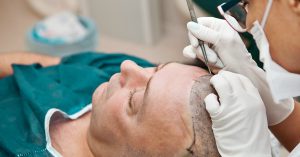
How Does the Procedure Work?
The hair transplant professional first assesses the amount of hair thinning and determines the best possible
donor site. The surrounding locks of the donor site must happen to be enough to hide possible scars, which is
usually among the common side effects of the procedure. Hair transplantation
After the assessment is complete, the surgeon proceeds to the transplantation. The patient can be administered
with sedative and local anaesthesia, although in some instances, general anaesthesia is furnished. The donor site
is then extensively cleaned and applied with antiseptic.Hair transplantation
If the FUE strategy is usually to be used, the surgeon and his team will take away the follicular unit one at a time,
leaving behind the looks of tiny dots. If it’s FUSS, the surgeon removes a strip of the scalp using a scalpel and
sews the scalp shut, allowing the nearby hair to cover it. The surgeon’s crew then begins to split up the scalp into
some micrografts made up of 5 hairs on the common.
With the hair prepared for transplant, the surgeon applies antiseptic to the recipient site and may make holes or
incisions where the follicles are transferred one at a time.
Depending on the volume of hair to be harvested and transplanted, the surgical procedure, which is performed
on a great outpatient basis, may take at least four to eight hours.
Possible Risks and Complications
The main risks associated with the procedure are long-lasting scarring and soreness or pain in both donor and
recipient sites following the procedure. Other unwanted effects such as bleeding, disease, uneven hair regrowth,
and hair thinning recurrence do happen but are extremely rare.
Hair transplant graft
Locks transplant grafts are generally performed under local anaesthetic. Each session of treatment can last from
two to eight hours, based on the number of hairs that happen to be transplanted.
It is common to transplant between 1,000 and 2,000 hair follicles in one session, but larger regions of hair loss
may require up to 4,000 follicles found in each session. A session may take several hours and several people tend
to have several separate sessions.
Flap surgery
Flap surgery is used if the wild hair transplant is comprehensive (for example, requires large tissue flaps rather
than tiny grafts). You may need to stay in hospital for this type of hair thinning surgery and standard anaesthesia will be needed.
Flap surgery involves:
• The surgeon implants balloon-like units (called tissue expanders) under the epidermis of a hair-bearing portion
of the scalp. The cells expanders happen to be inflated with more and more saline over weeks. This encourages
the region to grow more skin cells.
• After about 8 weeks, the scalp is continuing to grow enough extra pores and skin for the transplant surgery.
• The bald portion of the scalp is sliced and removed. The newly grown spot of the hair-bearing epidermis is
partly sliced away, shifted to its new area and stitched into place.
Since the flap is hardly ever fully severed from
the scalp, it should retain a great blood supply.
Scalp reduction surgery
Scalp reduction surgery is suitable to take care of bald areas on the trunk and the surface of the scalp, not
towards the leading of the scalp. The surgery includes:
Soon after hair transplant surgery
How you are feeling afterwards depends on the extent of medical procedures. After the operation, you may expect:
bruising and swelling
possible numbness
pain, throbbing and discomfort
a tight feeling in the scalp
to dress in dressings or bandages (a pressure bandage may be worn for just one or two days)
formation of small scabs over the treated regions of the scalp.
Complications of wild hair transplant surgery
This is simply not a complete list. For instance, your medical history or lifestyle may place you at increased threat
of certain complications. Get hold of your surgeon to learn more.
Self-care just after hair transplant surgery
Get guided by your surgeon. General self-care recommendations include:
• Follow all guidelines on caring for your wounds.
• Avoid training or any strenuous activity that could increase blood pressure, as this may produce your wounds to
bleed. Your surgeon may help you to steer clear of sex for approximately 10 days.
• Report any bleeding, extreme pain or uncommon symptoms to your surgeon.
Long-term outlook just after hair transplant surgery
Most hair transplants are powerful, although and it may take up to nine months because before the hair calls for root and
begins to fill in. It isn’t uncommon for the transplanted wild hair to fall out after countless months and regrow.
Once the head of hair begins to regrow, it will look natural for the reason that hair is transplanted in the way in
which the head of hair would normally grow for the reason of that location.
Most scars ought to be covered with hair and will be hard to see. Any visible scarring will become permanent but
should fade as time passes. Show patience – improvements to scars might take 12 months.
You will almost certainly need ‘touch up’ surgery to increase the look of your hair transplant.
Alternatives to hair transplant surgery
Non-surgical alternatives to wild hair transplant and surgery include:
overcome your concerns about your appearance and you’ll decide that you want yourself how you are.
Finding a head of hair transplant surgeon
• You may choose to ask your physician for advice on the right and reputable doctor or hospital where wild hair
transplants are performed.
• At your first consultation, you should talk to the surgeon about their training and experience. It is preferable to
have these methods done by an established professional who is specifically trained to execute hair transplant
medical procedures and has a large amount of experience in carrying out this sort of operation.